3.
Benbe 15 year s ago
Science Geek,
Almost. But if it was the case, everything would look like a rainbow.
In fact the satellite captures imagery in four steps: first, with a blue, then, with a green, then, with a red colour filter, and finishes without a filter, but the sensor used is a monochrome sensor, so we have three separate images for the three main colours and a fourth image for high resolution shades.
Because the plane was moving fast relative to Earth during the capture of the four consequent images it appeared on all of them but at different positions. Normally Google recaptures such images or corrects them from overlapping parts of the next pass-over, probably they oversaw something in this case.
Almost. But if it was the case, everything would look like a rainbow.
In fact the satellite captures imagery in four steps: first, with a blue, then, with a green, then, with a red colour filter, and finishes without a filter, but the sensor used is a monochrome sensor, so we have three separate images for the three main colours and a fourth image for high resolution shades.
Because the plane was moving fast relative to Earth during the capture of the four consequent images it appeared on all of them but at different positions. Normally Google recaptures such images or corrects them from overlapping parts of the next pass-over, probably they oversaw something in this case.
15.
LarryKing 15 year s ago
YOU ARE ALL WRONG:
The reason for the rainbow effect is called the baryon sweep caused by the cameras Heisenberg compensator which throws off the semi-round anti-proton inverse phasing crystal emanations. Then the developer adds a little pixie dust when turning the sonic screwdriver on the inductive plasma reactor. So simple you morons.
Is there Gold at the end of this rainbow ?
The reason for the rainbow effect is called the baryon sweep caused by the cameras Heisenberg compensator which throws off the semi-round anti-proton inverse phasing crystal emanations. Then the developer adds a little pixie dust when turning the sonic screwdriver on the inductive plasma reactor. So simple you morons.
Is there Gold at the end of this rainbow ?
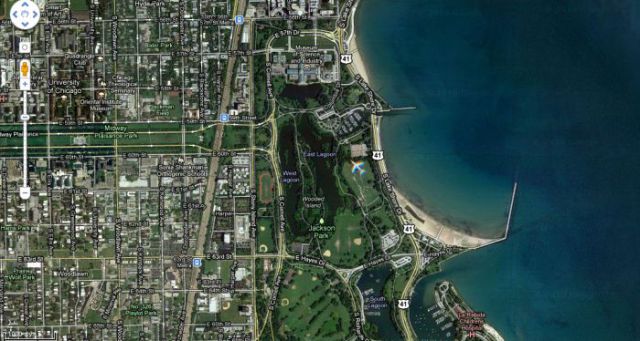
Almost. But if it was the case, everything would look like a rainbow.
In fact the satellite captures imagery in four steps: first, with a blue, then, with a green, then, with a red colour filter, and finishes without a filter, but the sensor used is a monochrome sensor, so we have three separate images for the three main colours and a fourth image for high resolution shades.
Because the plane was moving fast relative to Earth during the capture of the four consequent images it appeared on all of them but at different positions. Normally Google recaptures such images or corrects them from overlapping parts of the next pass-over, probably they oversaw something in this case.
cute
:)
The reason for the rainbow effect is called the baryon sweep caused by the cameras Heisenberg compensator which throws off the semi-round anti-proton inverse phasing crystal emanations. Then the developer adds a little pixie dust when turning the sonic screwdriver on the inductive plasma reactor. So simple you morons.
Is there Gold at the end of this rainbow ?