X
Comments to #3
All comments (X)
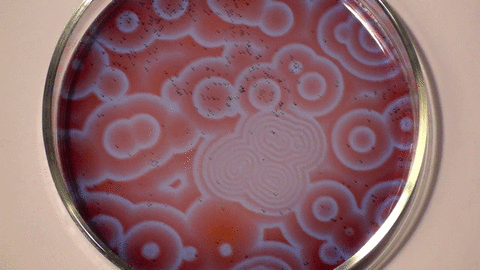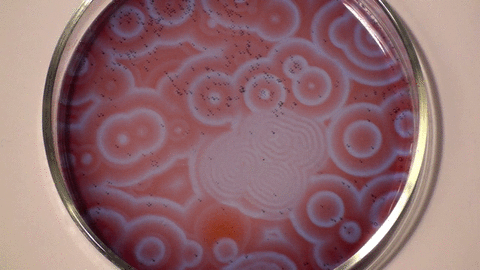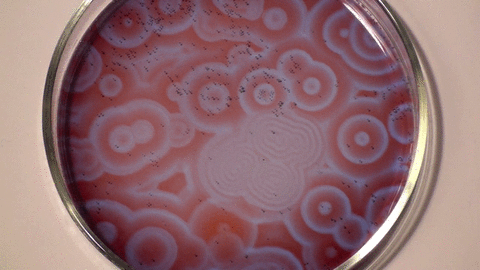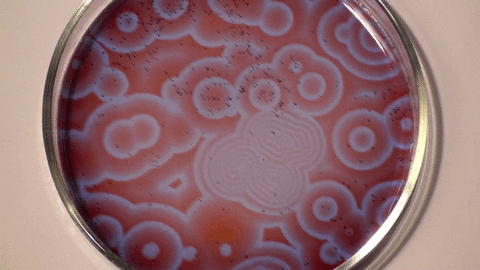
Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction
The mechanism for this reaction is very complex and is thought to involve around 18 different steps which have been the subject of a number of research papers. The classic BZ reaction involves potassium bromate, cerium(IV) sulfate, and propanedioic acid (aka malonic acid) in dilute sulfuric acid. The color changes are due to the oscillating oxidation state of cerium.