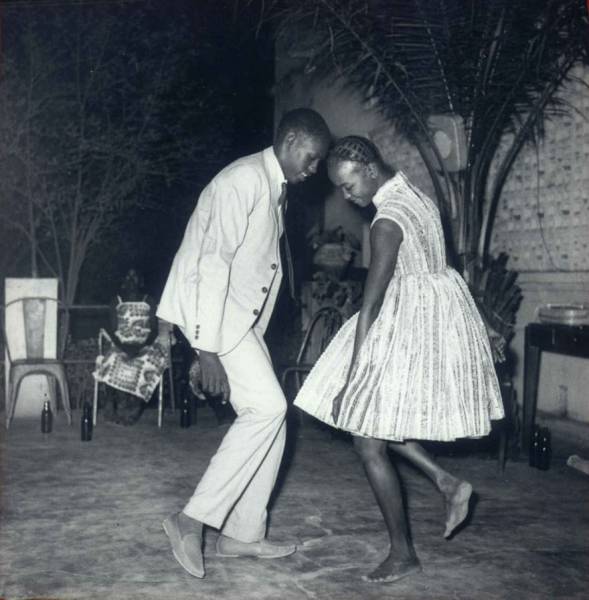
Nuit De Noel, Malick Sidibe, 1963 Malian photographer Malick Sidibé’s life followed the trajectory of his nation. He started out herding his family’s goats, then trained in jewelry making, painting and photography. As French colonial rule ended in 1960, he captured the subtle and profound changes reshaping his nation. Nicknamed the Eye of Bamako, Sidibé took thousands of photos that became a real-time chronicle of the euphoric zeitgeist gripping the capital, a document of a fleeting moment. “Everyone had to have the latest Paris style,” he observed of young people wearing flashy clothes, straddling Vespas and nuzzling in public as they embraced a world without shackles. On Christmas Eve in 1963, Sidibé happened on a young couple at a club, lost in each other’s eyes. What Sidibé called his “talent to observe” allowed him to capture their quiet intimacy, heads brushing as they grace an empty dance floor. “We were entering a new era, and people wanted to dance,” Sidibé said. “Music freed us. Suddenly, young men could get close to young women, hold them in their hands. Before, it was not allowed. And everyone wanted to be photographed dancing up close.”
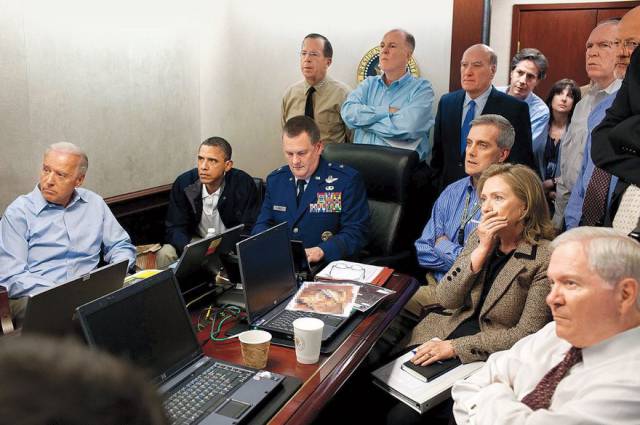
The Situation Room, Pete Souza, 2011 Official White House photographers document Presidents at play and at work, on the phone with world leaders and presiding over Oval Office meetings. But sometimes the unique access allows them to capture watershed moments that become our collective memory. On May 1, 2011, Pete Souza was inside the Situation Room as U.S. forces raided Osama bin Laden’s Pakistan compound and killed the terrorist leader. Yet Souza’s picture includes neither the raid nor bin Laden. Instead he captured those watching the secret operation in real time. President Barack Obama made the decision to launch the attack, but like everyone else in the room, he is a mere spectator to its execution. He stares, brow furrowed, at the raid unfolding on monitors. Secretary of State Hillary Clinton covers her mouth, waiting to see its outcome. In a national address that evening from the White House, Obama announced that bin Laden had been killed. Photographs of the dead body have never been released, leaving Souza’s photo and the tension it captured as the only public image of the mom
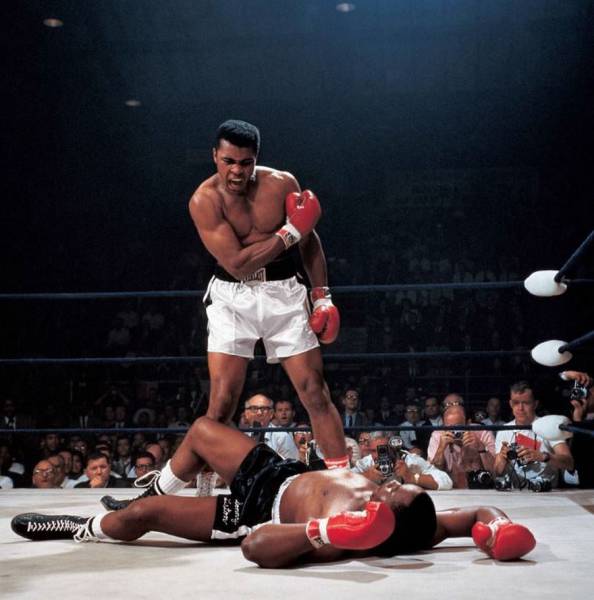
Muhammad Ali Vs. Sonny Liston, Neil Leifer, 1965 So much of great photography is being in the right spot at the right moment. That was what it was like for sports illustrated photographer Neil Leifer when he shot perhaps the greatest sports photo of the century. “I was obviously in the right seat, but what matters is I didn’t miss,” he later said. Leifer had taken that ringside spot in Lewiston, Maine, on May 25, 1965, as 23-year-old heavyweight boxing champion Muhammad Ali squared off against 34-year-old Sonny Liston, the man he’d snatched the title from the previous year. One minute and 44 seconds into the first round, Ali’s right fist connected with Liston’s chin and Liston went down. Leifer snapped the photo of the champ towering over his vanquished opponent and taunting him, “Get up and fight, sucker!” Powerful overhead lights and thick clouds of cigar smoke had turned the ring into the perfect studio, and Leifer took full advantage. His perfectly composed image captures Ali radiating the strength and poetic brashness that made him the nation’s most beloved and reviled athlete, at a moment when sports, politics and popular culture were being squarely battered in the tumult of the ’60s.
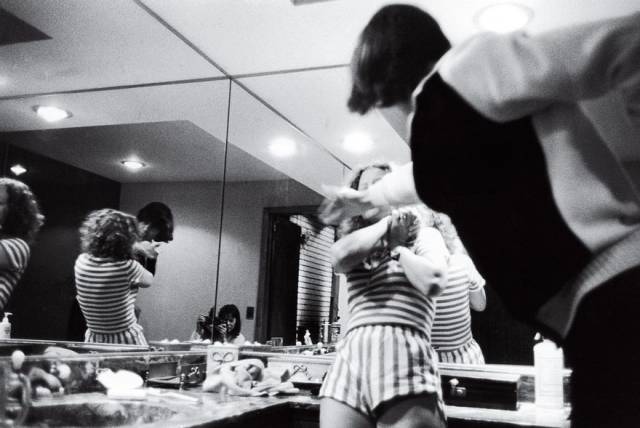
Behind Closed Doors, Donna Ferrato, 1982 There was nothing particularly special about Garth and Lisa or the violence that happened in the bathroom of their suburban New Jersey home one night in 1982. Enraged by a perceived slight, Garth beat his wife while she cowered in a corner. Such acts of intimate-partner violence are not uncommon, but they usually happen in private. This time another person was in the room, photographer Donna Ferrato. Ferrato, who had come to know the couple through a photo project on wealthy swingers, knew that simply bearing witness wasn’t enough. Her shutter clicked again and again. Ferrato approached magazine editors to publish the images, but all refused. So Ferrato did, in her 1991 book Living With the Enemy. The landmark volume chronicled domestic-violence episodes and their aftermaths, including those of the pseudonymous Garth and Lisa. Their real names are Elisabeth and Bengt; his identity was revealed for the first time as part of this project. Ferrato captured incidents and victims while living inside women’s shelters and shadowing police. Her work helped bring violence against women out of the shadows and forced policymakers to confront the issue. In 1994, Congress passed the Violence Against Women Act, increasing penalties against offenders and helping train police to treat it as a serious crime. Thanks to Ferrato, a private tragedy became a public cause.
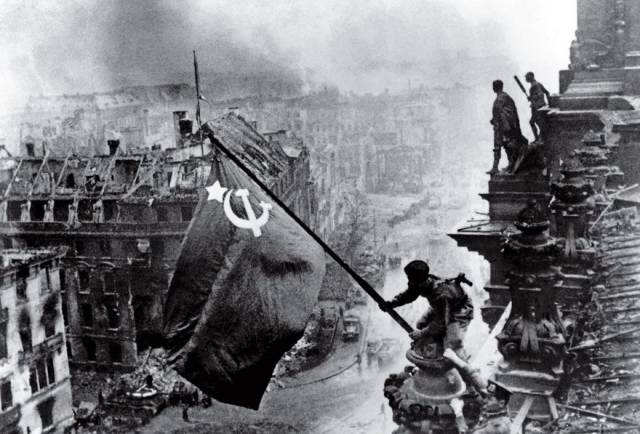
Raising A Flag Over The Reichstag, Yevgeny Khaldei, 1945 “This is what I was waiting for for 1,400 days,” the Ukrainian-born Yevgeny Khaldei said as he gazed at the ruins of Berlin on May 2, 1945. After four years of fighting and photographing across Eastern Europe, the Red Army soldier arrived in the heart of the Nazis’ homeland armed with his Leica III rangefinder and a massive Soviet flag that his uncle, a tailor, had fashioned for him from three red tablecloths. Adolf Hitler had committed suicide two days before, yet the war still raged as Khaldei made his way to the Reichstag. There he told three soldiers to join him, and they clambered up broken stairs onto the parliament building’s blood-soaked parapet. Gazing through his camera, Khaldei knew he had the shot he had hoped for: “I was euphoric.” In printing, Khaldei dramatized the image by intensifying the smoke and darkening the sky—even scratching out part of the negative—to craft a romanticized scene that was part reality, part artifice and all patriotism. Published in the Russian magazine Ogonek, the image became an instant propaganda icon. And no wonder. The flag jutting from the heart of the enemy exalted the nobility of communism, proclaimed the Soviets the new overlords and hinted that by lowering the curtain of war, Premier Joseph Stalin would soon hoist a cold new iron one across the land.
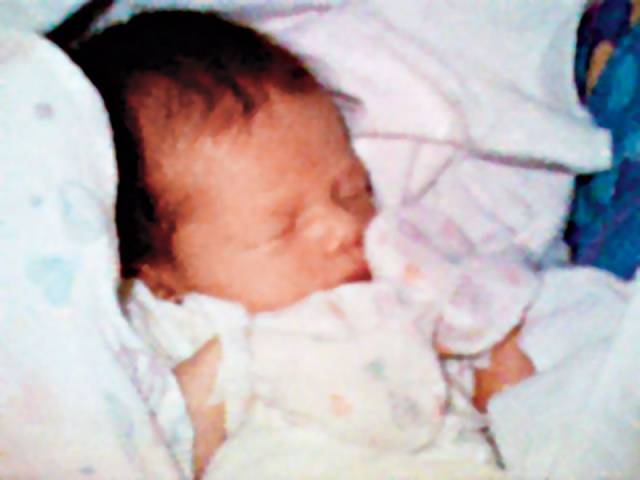
First Cell-Phone Picture, Philippe Kahn, 1997 Boredom can be a powerful incentive. In 1997, Philippe Kahn was stuck in a Northern California maternity ward with nothing to do. The software entrepreneur had been shooed away by his wife while she birthed their daughter, Sophie. So Kahn, who had been tinkering with technologies that share images instantly, jerry-built a device that could send a photo of his newborn to friends and family—in real time. Like any invention, the setup was crude: a digital camera connected to his flip-top cell phone, synched by a few lines of code he’d written on his laptop in the hospital. But the effect has transformed the world: Kahn’s device captured his daughter’s first moments and transmitted them instantly to more than 2,000 people. Kahn soon refined his ad hoc prototype, and in 2000 Sharp used his technology to release the first commercially available integrated camera phone, in Japan. The phones were introduced to the U.S. market a few years later and soon became ubiquitous. Kahn’s invention forever altered how we communicate, perceive and experience the world and laid the groundwork for smartphones and photo-sharing applications like Instagram and Snapchat. Phones are now used to send hundreds of millions of images around the world every day—including a fair number of baby pictures.
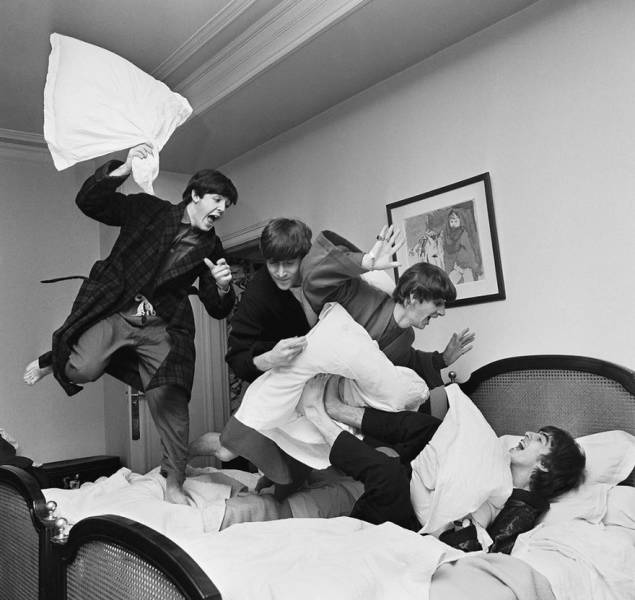
The Pillow Fight, Harry Benson, 1964 Harry Benson didn’t want to meet the Beatles. The Glasgow-born photographer had plans to cover a news story in Africa when he was assigned to photograph the musicians in Paris. “I took myself for a serious journalist and I didn’t want to cover a rock ’n’ roll story,” he scoffed. But once he met the boys from Liverpool and heard them play, Benson had no desire to leave. “I thought, ‘God, I’m on the right story.’ ” The Beatles were on the cusp of greatness, and Benson was in the middle of it. His pillow-fight photo, taken in the swanky George V Hotel the night the band found out “I Want to Hold Your Hand” hit No. 1 in the U.S., freezes John, Paul, George and Ringo in an exuberant cascade of boyish talent—and perhaps their last moment of unbridled innocence. It captures the sheer joy, happiness and optimism that would be embraced as Beatlemania and that helped lift America’s morale just 11 weeks after John F. Kennedy’s assassination. The following month, Benson accompanied the Fab Four as they flew to New York City to appear on The Ed Sullivan Show, kick-starting the British Invasion. The trip led to decades of collaboration with the group and, as Benson later recalled, “I was so close to not being there.”
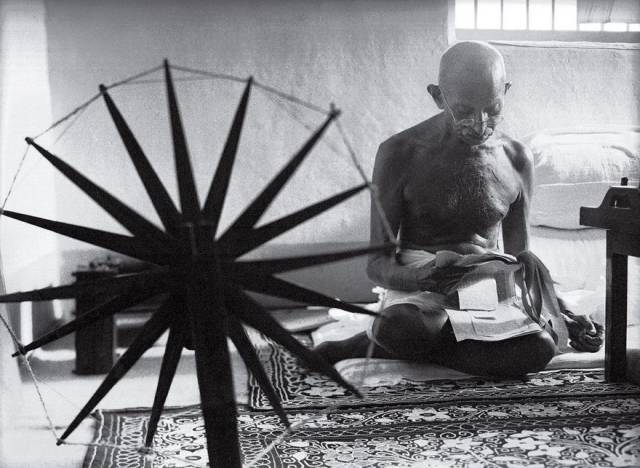
Gandhi And The Spinning Wheel, Margaret Bourke-White, 1946 When the British held Mohandas Gandhi prisoner at Yeravda prison in Pune, India, from 1932 to 1933, the nationalist leader made his own thread with a charkha, a portable spinning wheel. The practice evolved from a source of personal comfort during captivity into a touchstone of the campaign for independence, with Gandhi encouraging his countrymen to make their own homespun cloth instead of buying British goods. By the time Margaret Bourke-White came to Gandhi’s compound for a life article on India’s leaders, spinning was so bound up with Gandhi’s identity that his secretary, Pyarelal Nayyar, told Bourke-White that she had to learn the craft before photographing the leader. Bourke-White’s picture of Gandhi reading the news alongside his charkha never appeared in the article for which it was taken, but less than two years later life featured the photo prominently in a tribute published after Gandhi’s assassination. It soon became an indelible image, the slain civil-disobedience crusader with his most potent symbol, and helped solidify the perception of Gandhi outside the subcontinent as a saintly man of peace.
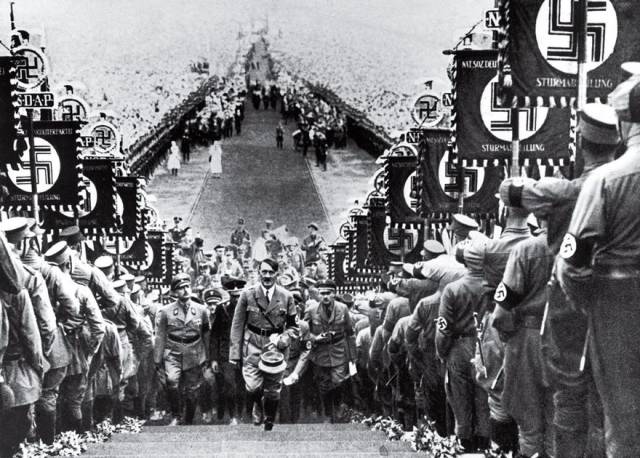
Hitler At A Nazi Party Rally, Heinrich Hoffmann, 1934 Spectacle was like oxygen for the Nazis, and Heinrich Hoffmann was instrumental in staging Hitler’s growing pageant of power. Hoffmann, who joined the party in 1920 and became Hitler’s personal photographer and confidant, was charged with choreographing the regime’s propaganda carnivals and selling them to a wounded German public. Nowhere did Hoffmann do it better than on September 30, 1934, in his rigidly symmetrical photo at the Bückeberg Harvest Festival, where the Mephistophelian Führer swaggers at the center of a grand Wagnerian fantasy of adoring and heiling troops. By capturing this and so many other extravaganzas, Hoffmann—who took more than 2 million photos of his boss—fed the regime’s vast propaganda machine and spread its demonic dream. Such images were all-pervasive in Hitler’s Reich, which shrewdly used Hoffman’s photos, the stark graphics on Nazi banners and the films of Leni Riefenstahl to make Aryanism seem worthy of godlike worship. Humiliated by World War I, punishing reparations and the Great Depression, a nation eager to reclaim its sense of self was rallied by Hitler’s visage and his seemingly invincible men aching to right wrongs. Hoffmann’s expertly rendered propaganda is a testament to photography’s power to move nations and plunge a world into war.
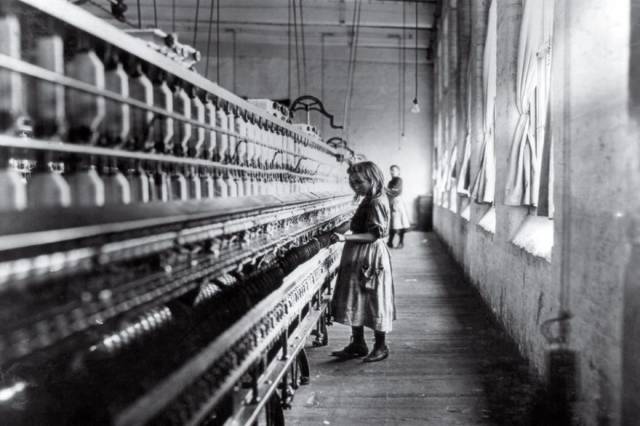
Cotton Mill Girl, Lewis Hine, 1908 Working as an investigative photographer for the National Child Labor Committee, Lewis Hine believed that images of child labor would force citizens to demand change. The muckraker conned his way into mills and factories from Massachusetts to South Carolina by posing as a Bible seller, insurance agent or industrial photographer in order to tell the plight of nearly 2 million children. Carting around a large-format camera and jotting down information in a hidden notebook, Hine recorded children laboring in meatpacking houses, coal mines and canneries, and in November 1908 he came upon Sadie Pfeifer, who embodied the world he exposed. A 48-inch-tall wisp of a girl, she was “one of the many small children at work” manning a gargantuan cotton-spinning machine in Lancaster, S.C. Since Hine often had to lie to get his shots, he made “double-sure that my photo data was 100% pure—no retouching or fakery of any kind.” His images of children as young as 8 dwarfed by the cogs of a cold, mechanized universe squarely set the horrors of child labor before the public, leading to regulatory legislation and cutting the number of child laborers nearly in half from 1910 to 1920.
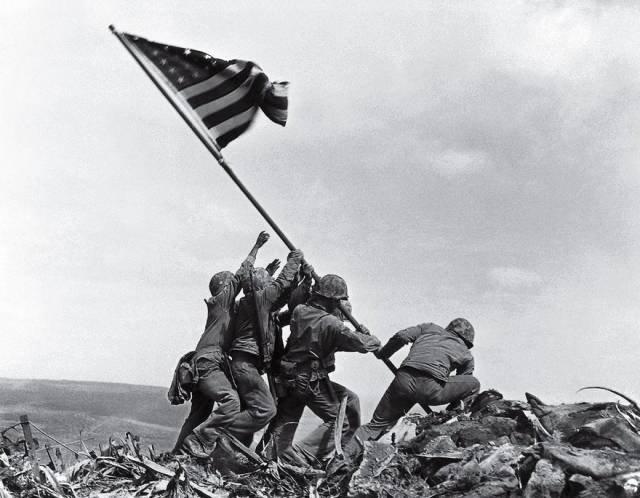
Flag Raising On Iwo Jima, Joe Rosenthal, 1945 It is but a speck of an island 760 miles south of Tokyo, a volcanic pile that blocked the Allies’ march toward Japan. The Americans needed Iwo Jima as an air base, but the Japanese had dug in. U.S. troops landed on February 19, 1945, beginning a month of fighting that claimed the lives of 6,800 Americans and 21,000 Japanese. On the fifth day of battle, the Marines captured Mount Suribachi. An American flag was quickly raised, but a commander called for a bigger one, in part to inspire his men and demoralize his opponents. Associated Press photographer Joe Rosenthal lugged his bulky Speed Graphic camera to the top, and as five Marines and a Navy corpsman prepared to hoist the Stars and Stripes, Rosenthal stepped back to get a better frame—and almost missed the shot. “The sky was overcast,” he later wrote of what has become one of the most recognizable images of war. “The wind just whipped the flag out over the heads of the group, and at their feet the disrupted terrain and the broken stalks of the shrubbery exemplified the turbulence of war.” Two days later Rosenthal’s photo was splashed on front pages across the U.S., where it was quickly embraced as a symbol of unity in the long-fought war. The picture, which earned Rosenthal a Pulitzer Prize, so resonated that it was made into a postage stamp and cast as a 100-ton bronze memorial.
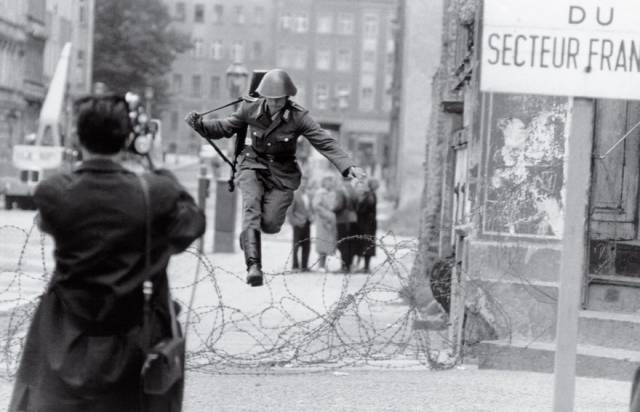
Leap Into Freedom, Peter Leibing, 1961 Following World War II, the conquering Allied governments carved Berlin into four occupation zones. Yet each part was not equal, and from 1949 to 1961 some 2.5 million East Germans fled the Soviet section in search of freedom. To stop the flow, East German leader Walter Ulbricht had a barbed-wire-and-cinder-block barrier thrown up in early August 1961. A few days later, Associated Press photographer Peter Leibing was tipped off that a defection might happen. He and other cameramen gathered and watched as a West Berlin crowd enticed 19-year-old border guard Hans Conrad Schumann, yelling to him, “Come on over!” Schumann, who later said he did not want to “live enclosed,” suddenly ran for the barricade. As he cleared the sharp wires he dropped his rifle and was whisked away. Sent out across the AP wire, Leibing’s photo ran on front pages across the world. It made Schumann, reportedly the first known East German soldier to flee, into a poster child for those yearning to be free, while lending urgency to East Germany’s push for a more permanent Berlin Wall. Schumann was sadly haunted by the weight of it all. While he quietly lived in the West, he could not grapple with his unintended stature as a symbol of freedom, and he committed suicide in 1998.
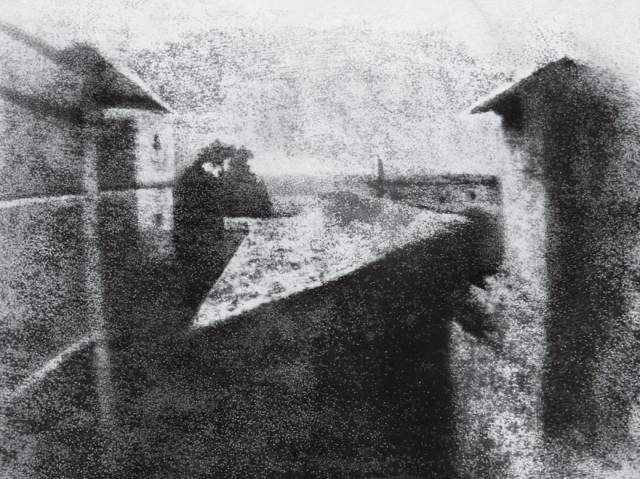
View From The Window At Le Gras, Joseph Nicéphore Niépce, 1826 It took a unique combination of ingenuity and curiosity to produce the first known photograph, so it’s fitting that the man who made it was an inventor and not an artist. In the 1820s, Joseph Nicéphore Niépce had become fascinated with the printing method of lithography, in which images drawn on stone could be reproduced using oil-based ink. Searching for other ways to produce images, Niépce set up a device called a camera obscura, which captured and projected scenes illuminated by sunlight, and trained it on the view outside his studio window in eastern France. The scene was cast on a treated pewter plate that, after many hours, retained a crude copy of the buildings and rooftops outside. The result was the first known permanent photograph. It is no overstatement to say that Niépce’s achievement laid the groundwork for the development of photography. Later, he worked with artist Louis Daguerre, whose sharper daguerreotype images marked photography’s next major advancement.
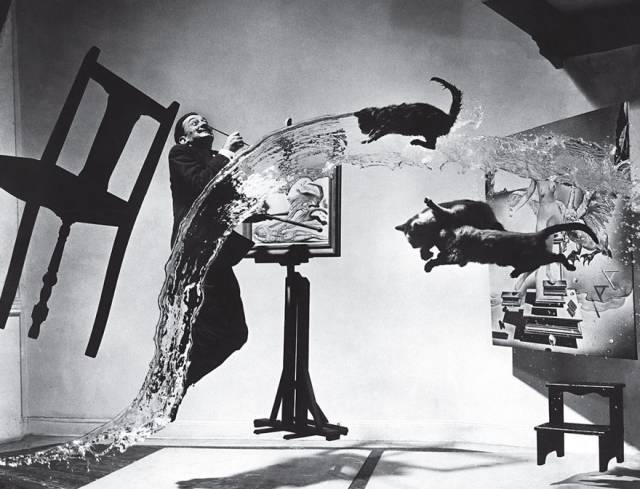
Dalí Atomicus, Philippe Halsman, 1948 Capturing the essence of those he photographed was Philippe Halsman’s life’s work. So when Halsman set out to shoot his friend and longtime collaborator the Surrealist painter Salvador Dalí, he knew a simple seated portrait would not suffice. Inspired by Dalí’s painting Leda Atomica, Halsman created an elaborate scene to surround the artist that included the original work, a floating chair and an in-progress easel suspended by thin wires. Assistants, including Halsman’s wife and young daughter Irene, stood out of the frame and, on the photographer’s count, threw three cats and a bucket of water into the air while Dalí leaped up. It took the assembled cast 26 takes to capture a composition that satisfied Halsman. And no wonder. The final result, published in LIFE, evokes Dalí’s own work. The artist even painted an image directly onto the print before publication. Before Halsman, portrait photography was often stilted and softly blurred, with a clear sense of detachment between the photographer and the subject. Halsman’s approach, to bring subjects such as Albert Einstein, Marilyn Monroe and Alfred Hitchcock into sharp focus as they moved before the camera, redefined portrait photography and inspired generations of photographers to collaborate with their subjects.
The Hindenburg Disaster, Sam Shere, 1937 Zeppelins were majestic skyliners, luxurious behemoths that signified wealth and power. The arrival of these ships was news, which is why Sam Shere of the International News Photos service was waiting in the rain at the Lakehurst, N.J., Naval Air Station on May 6, 1937, for the 804-foot-long LZ 129 Hindenburg to drift in from Frankfurt. Suddenly, as the assembled media watched, the grand ship’s flammable hydrogen caught fire, causing it to spectacularly burst into bright yellow flames and kill 36 people. Shere was one of nearly two dozen still and newsreel photographers who scrambled to document the fast-moving tragedy. But it is his image, with its stark immediacy and horrible grandeur, that has endured as the most famous—owing to its publication on front pages around the world and in LIFE and, more than three decades later, its use on the cover of the first Led Zeppelin album. The crash helped bring the age of the airships to a close, and Shere’s powerful photograph of one of the world’s most formative early air disasters persists as a cautionary reminder of how human fallibility can lead to death and destruction. Almost as famous as Shere’s photo is the anguished voice of Chicago radio announcer Herbert Morrison, who cried as he watched people tumbling through the air, “It is bursting into flames ... This is terrible. This is one of the worst catastrophes in the world ... Oh, the humanity!”
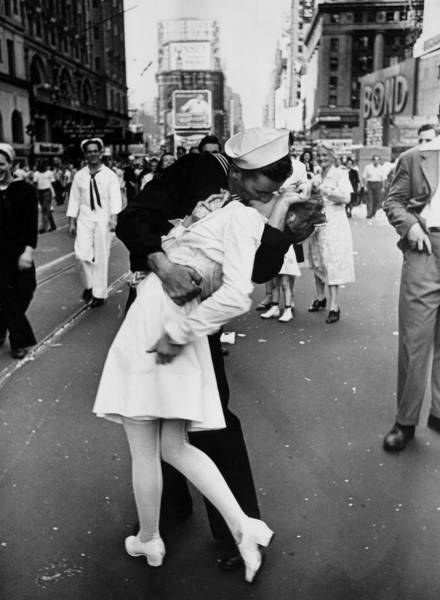
V-J Day In Times Square, Alfred Eisenstaedt, 1945 At its best, photography captures fleeting snippets that crystallize the hope, anguish, wonder and joy of life. Alfred Eisenstaedt, one of the first four photographers hired by LIFE magazine, made it his mission “to find and catch the storytelling moment.” He didn’t have to go far for it when World War II ended on August 14, 1945. Taking in the mood on the streets of New York City, Eisenstaedt soon found himself in the joyous tumult of Times Square. As he searched for subjects, a sailor in front of him grabbed hold of a nurse, tilted her back and kissed her. Eisenstaedt’s photograph of that passionate swoop distilled the relief and promise of that momentous day in a single moment of unbridled joy (although some argue today that it should be seen as a case of sexual assault). His beautiful image has become the most famous and frequently reproduced picture of the 20th century, and it forms the basis of our collective memory of that transformative moment in world history. “People tell me that when I’m in heaven,” Eisenstaedt said, “they will remember this picture.”
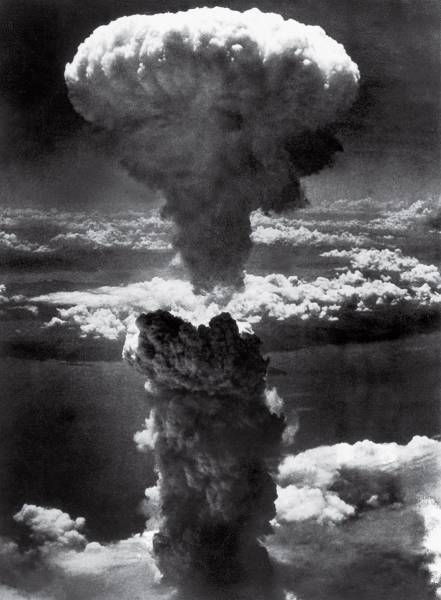
Mushroom Cloud Over Nagasaki, Lieutenant Charles Levy, 1945 Three days after an atomic bomb nicknamed Little Boy obliterated Hiroshima, Japan, U.S. forces dropped an even more powerful weapon dubbed Fat Man on Nagasaki. The explosion shot up a 45,000-foot-high column of radioactive dust and debris. “We saw this big plume climbing up, up into the sky,” recalled Lieutenant Charles Levy, the bombardier, who was knocked over by the blow from the 20-kiloton weapon. “It was purple, red, white, all colors—something like boiling coffee. It looked alive.” The officer then shot 16 photographs of the new weapon’s awful power as it yanked the life out of some 80,000 people in the city on the Urakami River. Six days later, the two bombs forced Emperor Hirohito to announce Japan’s unconditional surrender in World War II. Officials censored photos of the bomb’s devastation, but Levy’s image—the only one to show the full scale of the mushroom cloud from the air—was circulated widely. The effect shaped American opinion in favor of the nuclear bomb, leading the nation to celebrate the atomic age and proving, yet again, that history is written by the victors.
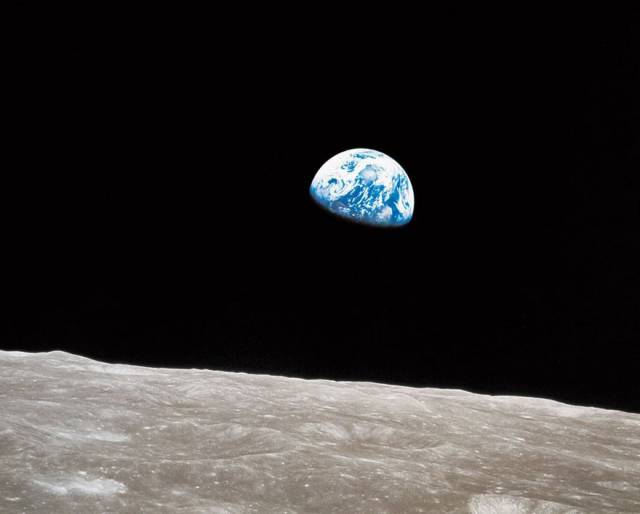
Earthrise, William Anders, NASA, 1968 It’s never easy to identify the moment a hinge turns in history. When it comes to humanity’s first true grasp of the beauty, fragility and loneliness of our world, however, we know the precise instant. It was on December 24, 1968, exactly 75 hours, 48 minutes and 41 seconds after the Apollo 8 spacecraft lifted off from Cape Canaveral en route to becoming the first manned mission to orbit the moon. Astronauts Frank Borman, Jim Lovell and Bill Anders entered lunar orbit on Christmas Eve of what had been a bloody, war-torn year for America. At the beginning of the fourth of 10 orbits, their spacecraft was emerging from the far side of the moon when a view of the blue-white planet filled one of the hatch windows. “Oh, my God! Look at that picture over there! Here’s the Earth coming up. Wow, is that pretty!” Anders exclaimed. He snapped a picture—in black and white. Lovell scrambled to find a color canister. “Well, I think we missed it,” Anders said. Lovell looked through windows three and four. “Hey, I got it right here!” he exclaimed. A weightless Anders shot to where Lovell was floating and fired his Hasselblad. “You got it?” Lovell asked. “Yep,” Anders answered. The image—our first full-color view of our planet from off of it—helped to launch the environmental movement. And, just as important, it helped human beings recognize that in a cold and punishing cosmos, we’ve got it pretty good.
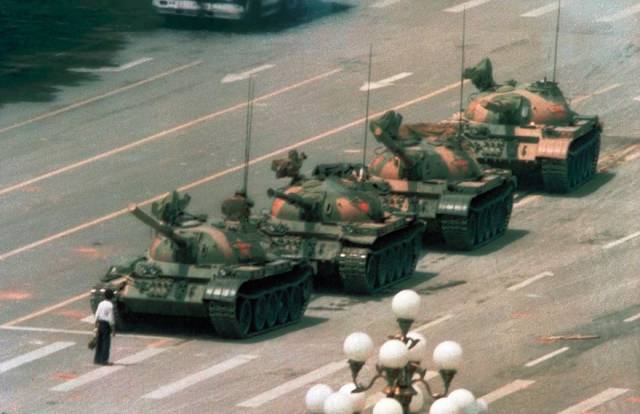
Tank Man, Jeff Widener, 1989 On the morning of June 5, 1989, photographer Jeff Widener was perched on a sixth-floor balcony of the Beijing Hotel. It was a day after the Tiananmen Square massacre, when Chinese troops attacked pro-democracy demonstrators camped on the plaza, and the Associated Press sent Widener to document the aftermath. As he photographed bloody victims, passersby on bicycles and the occasional scorched bus, a column of tanks began rolling out of the plaza. Widener lined up his lens just as a man carrying shopping bags stepped in front of the war machines, waving his arms and refusing to move. The tanks tried to go around the man, but he stepped back into their path, climbing atop one briefly. Widener assumed the man would be killed, but the tanks held their fire. Eventually the man was whisked away, but not before Widener immortalized his singular act of resistance. Others also captured the scene, but Widener’s image was transmitted over the AP wire and appeared on front pages all over the world. Decades after Tank Man became a global hero, he remains unidentified. The anonymity makes the photograph all the more universal, a symbol of resistance to unjust regimes everywhere.
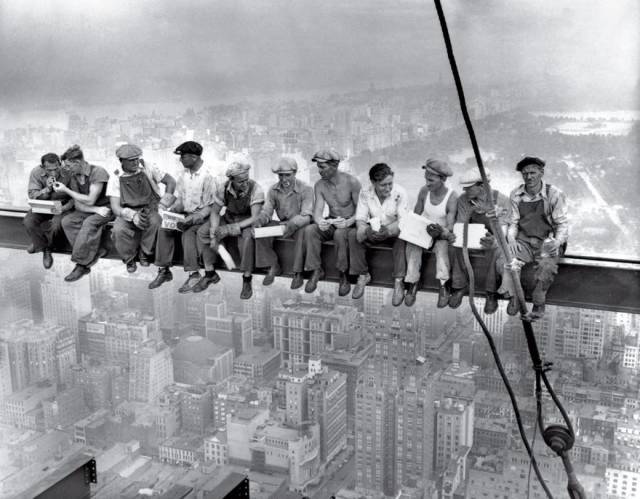
Lunch Atop A Skyscraper, 1932 It’s the most perilous yet playful lunch break ever captured: 11 men casually eating, chatting and sneaking a smoke as if they weren’t 840 feet above Manhattan with nothing but a thin beam keeping them aloft. That comfort is real; the men are among the construction workers who helped build Rockefeller Center. But the picture, taken on the 69th floor of the flagship RCA Building (now the GE Building), was staged as part of a promotional campaign for the massive skyscraper complex. While the photographer and the identities of most of the subjects remain a mystery—the photographers Charles C. Ebbets, Thomas Kelley and William Leftwich were all present that day, and it’s not known which one took it—there isn’t an ironworker in New York City who doesn’t see the picture as a badge of their bold tribe. In that way they are not alone. By thumbing its nose at both danger and the Depression, Lunch Atop a Skyscraper came to symbolize American resilience and ambition at a time when both were desperately needed. It has since become an iconic emblem of the city in which it was taken, affirming the romantic belief that New York is a place unafraid to tackle projects that would cow less brazen cities. And like all symbols in a city built on hustle, Lunch Atop a Skyscraper has spawned its own economy. It is the Corbis photo agency’s most reproduced image. And good luck walking through Times Square without someone hawking it on a mug, magnet or T-shirt.
Camille Clifford posing for photographer Charles Gibson after winning a contest held by Gibson as he looked for the perfect bodied woman in 1901. She won the event at the age of just 16. She is around 18-20 in this picture. Her ridiculous curves landed her $2000 US from the contest, and a few modeling shoots with Gibson and even films in England and the US the next few years. The Belgian born beauty quit as quickly as she began to settle down in 1906 at the age of 21.
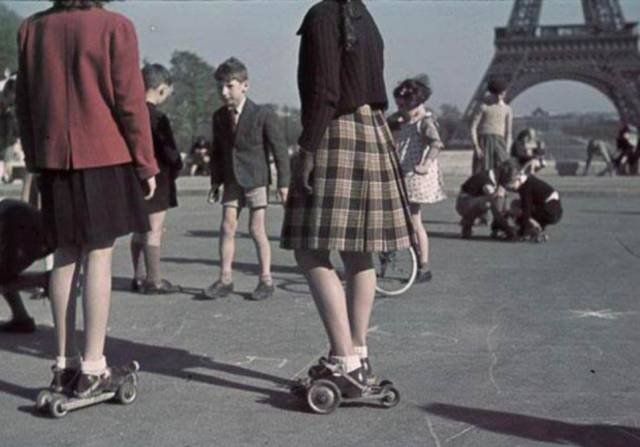
Children playing on an early version of roller skates in Paris, France in 1941. Pictures like these were actually taken by either Germans or hired French photographers to use as propaganda showing a happy French capitol under Nazi occupation.
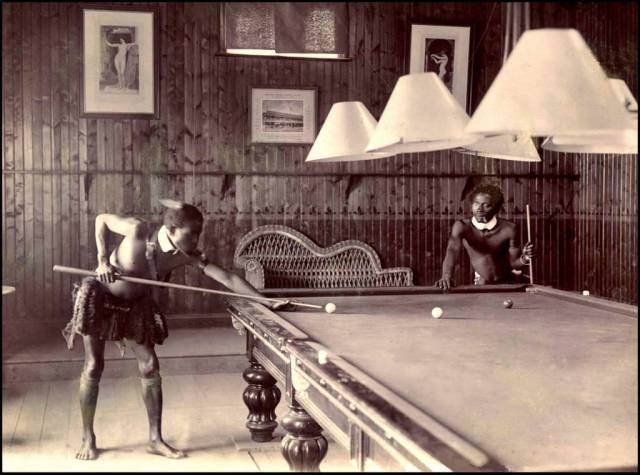
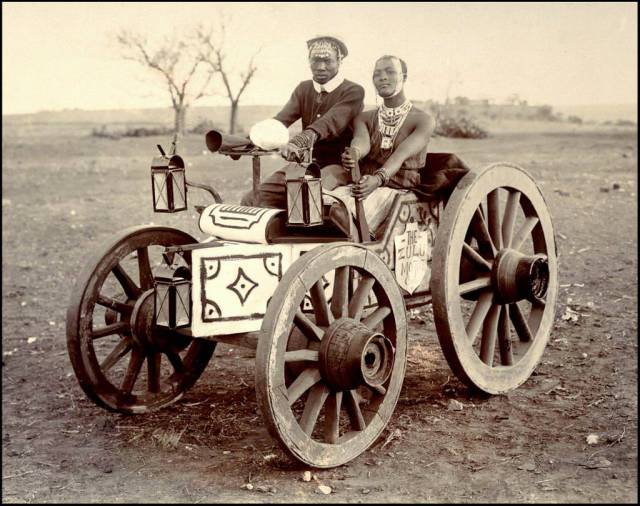
Two African Tribesmen pretending to be their colonial brethren playing pool in a town near what was the Zulu Empire in South Africa in 1903. Notice the eye piece and fake collars? There is a number of these pictures of the tribesmen and women doing everyday European and colonial activities.
Here is another picture from that genre. This is a picture of a Zulu couple in a Zulu Motor Cab in 1903.
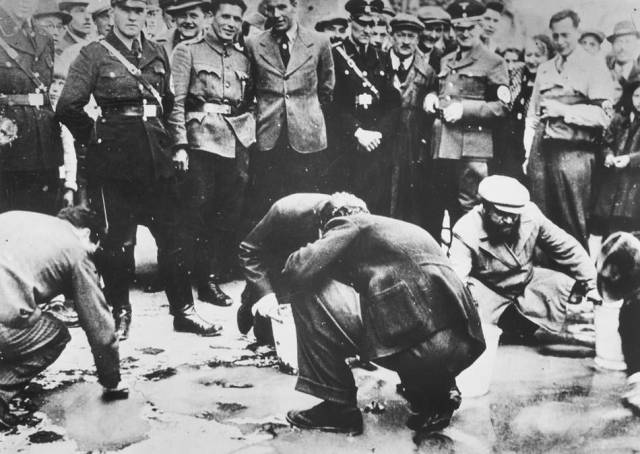
A crowd gathers to laugh at Jews who are forced to clean the pavement in Vienna, Austria in 1938. This would be the beginning of forceful manual labor, constant abuse, deportation and death for the Jews. Despite was was later said you can clearly see that civilians participated in the process.
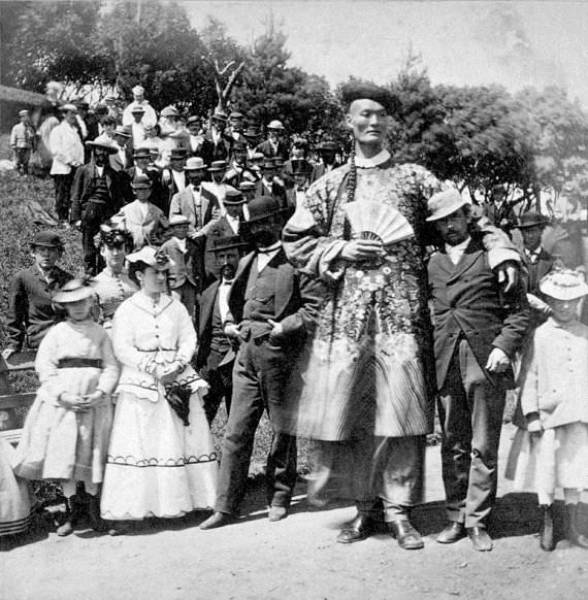
Zhan Shichai touring somewhere in the US in 1868. Known as Chang the Giant, this Chinese man was believed to be over 8 feet tall, and possibly was the tallest man to be photographed, but was never verified for his exact height. He left China in 1865, touring Europe, the US, and Australia. He retired in 1878 and died in 1892 at age 52.
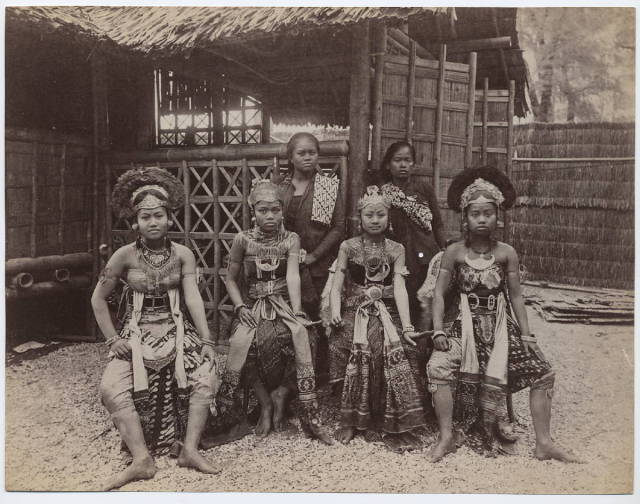
Women imported from Thailand pose for a picture at an exhibition in what would be know as a Human Zoo in Paris, France in 1889. Human Zoos had people from Africa, Asia, certain islands, even American communities. These Zoos were very prevalent in Europe and the US for patrons to go see the exhibitions of people "in their natural habitat". It got worse, certain women from some areas, especially Africa, were imported just for their figures. It was a humiliating and degrading display that lasted from around the 1850s all the way up until the last one closed in Belgium in 1958.
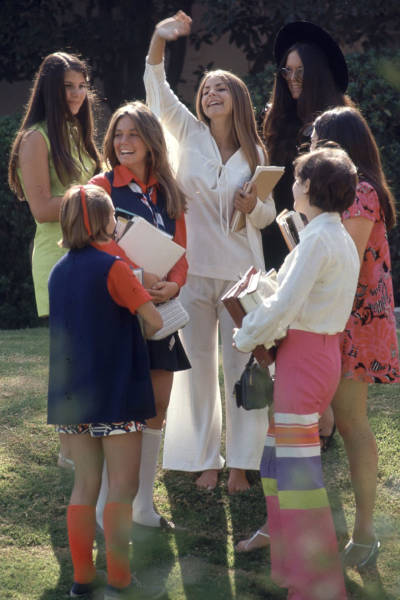
College girls hang out in California, US in 1969. This picture is terrific in showing many of the different fashions of the time period for women. From bell bottoms, to miniskirts, to the artsy look of the girl in the back, all common across America during this time.
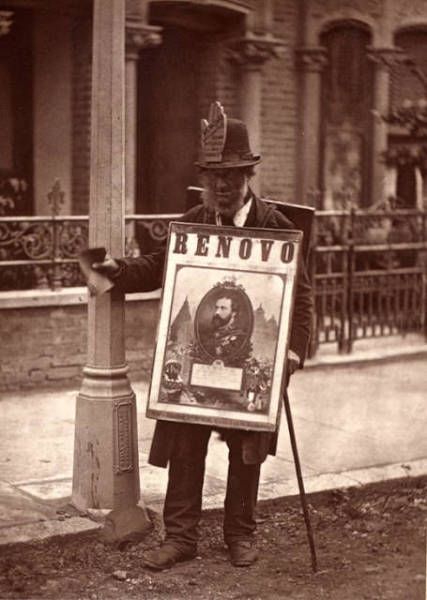
A boardman photographed in London, England in 1877. This was part of a series called "Street Life in London" by photographer John Thomson. Men such as these were often quite poor, and sometimes were even trampled by carriages on busy streets as they were forced by police to stay off the sidewalk.
People take to the streets in Washinton D.C., US to protest against any aggression that could lead to war during the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962. The Soviets wanted to put nuclear missiles in Cuba for first strike capabilities against the US in the event of war. Cuba, having gone communist with Castro rising to power, would be blockaded, and a 13 day standoff took place. Interesting note, the US saw the missiles well before they could be fired, and chose not to destroy them. This was a decision John F Kennedy made, against the wishes of virtually every military advisor he had. This allowed the missiles to become operational and also the possibility of half the East Coast to be destroyed. War was averted at the last minute through back door channels that had both countries disarm and remove missiles in key locations (Cuba for the USSR and Turkey for the US).
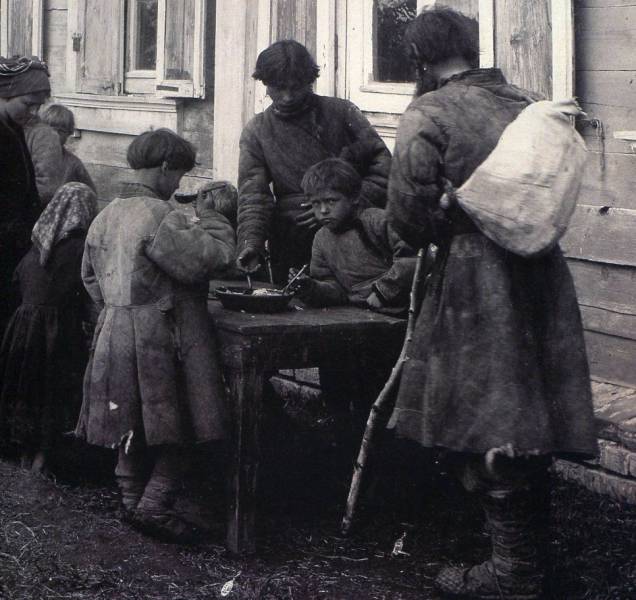
Children share a bowl of food in Moscow, Russia in the early 1900s. This picture and numerous others were taken by Maxim P Dmitriev who documented the incredibly poor conditions of peasants as well as everyday life from all over Russia. The images paint a very sad picture of the tough life of the poor.
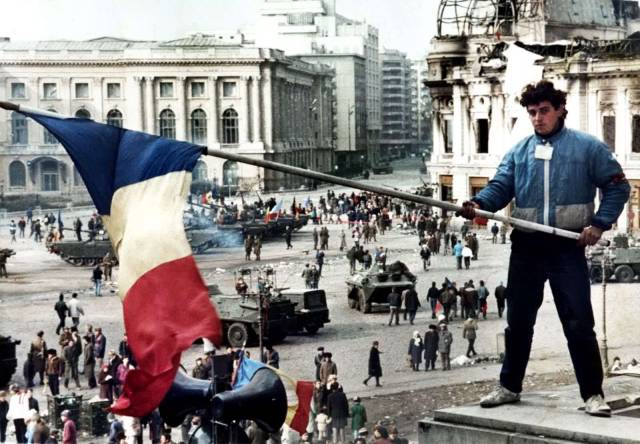
A Romanian citizen waves his flag as the center of Bucharest is captured by Revolutionary Forces during the Romanian Revolution in 1989. In a fast and strong move, Revolutionary Forces moved into the city and overthrew the communist regime, executing their former dictator and his wife. Up to 1200 people were killed in the 11 days of fighting, with the bulk of the government forces turning on the regime. Numerous images has everyday citizens joining the uprising. They would appear on tanks, in large scale marches, or even behind Revolutionary soldiers during attacks. It was a well documented uprising as the last of the Soviet Blocks of the Warsaw Pact in Europe came to an end.
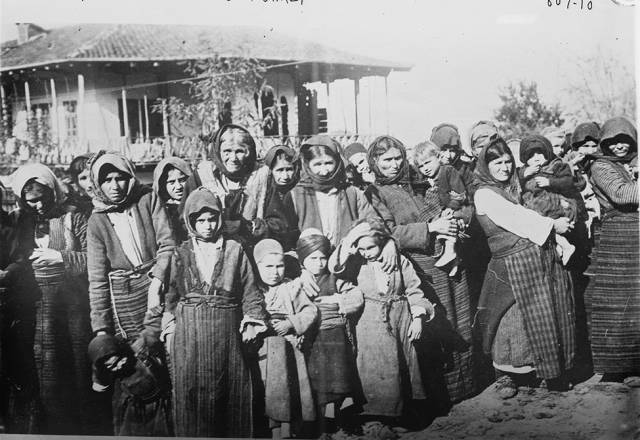
Armenian women with their children in a concentration camp in Turkey (notice the barbed wire in the background) as part of the Ottoman Empire in 1915. This was during the Armenian Genocide as the Turks systematically wiped out up to 1.5 million Armenians. The women in this picture would eventually be separated from their children. Turkey to this day still refuses to acknowledge the genocide.
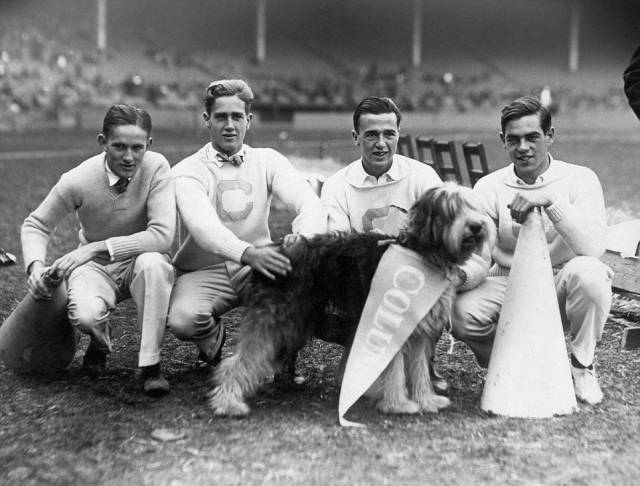
Columbia University cheerleaders with their four-legged mascot, Peter, at the Thanksgiving Day American football game in New York City, US in 1924. Originally, all cheerleading squads were men. In fact, there was a push to keep it so for many years, but eventually it was integrated with women in the 1930s who now dominate cheer squads throughout the US. To help entertain the crowds, routines were introduced. Eventually it turned into far more of a physical competitive sport than just cheering for your schools team on the sidelines. Pro teams often just employ women, but college squads in particular are often mixed with men and women and the routines just keep getting more and more complex requiring tough gymnastics moves and throws.
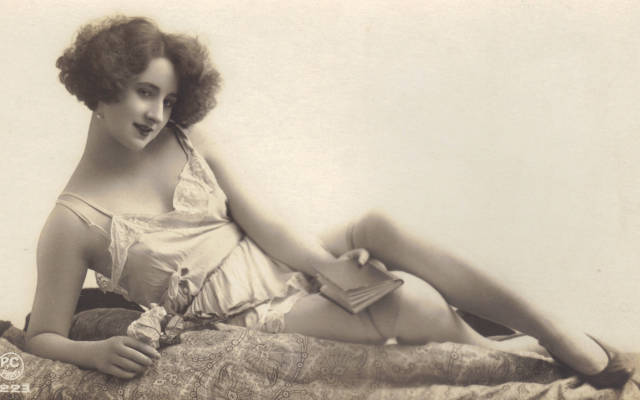
A model poses in Paris, France in 1922. Such risqué pictures were very prevalent especially in France. Often you could see similar pictures on postcards from that time.
An exhausted trader at the end of the worst day in stock market history, “Black Monday”, October 19, 1987. After “Black Monday”, stock exchanges instituted circuit breakers, or trading pauses, when there are large declines.
By the end of October, stock markets in Hong Kong, Australia, Spain, the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada had fallen 45.5%, 41.8%, 31%, 26.45%, 22.68% and 22.5% respectively. New Zealand’s market was hit especially hard, falling about 60% from its 1987 peak
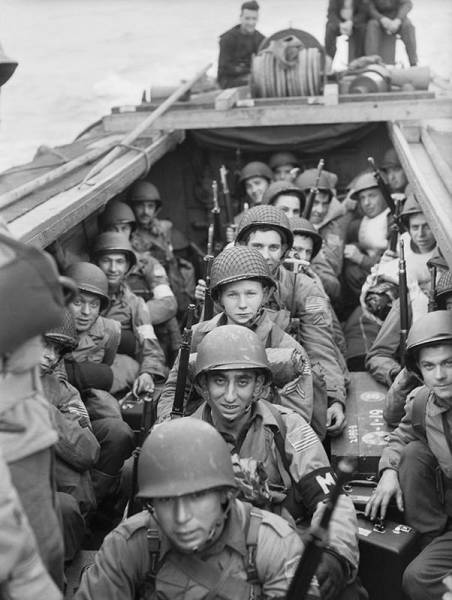
American troops on board a landing craft heading for the beaches at Oran in Algeria during Operation ‘Torch’, November 1942
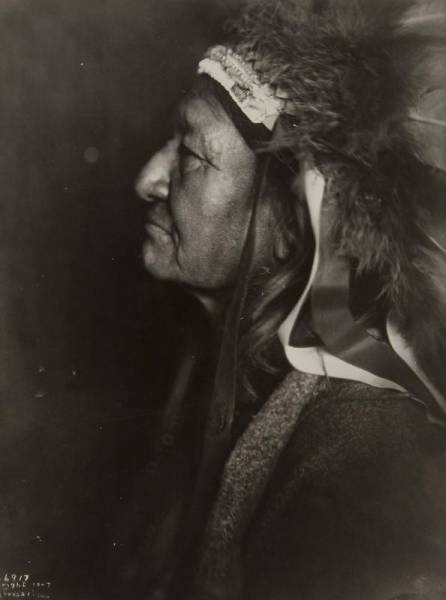
Two Moons, one of the Cheyenne chiefs who took part in the Battle of the Little Bighorn against the United States Army, 1910
Two Moons was the son of Carries the Otter, an Arikara captive who married into the Cheyenne tribe. Perhaps known best for his participation in battles such as the Battle of the Rosebud against General Crook on June 17, 1876, in the Montana Territory, the Battle of Little Big Horn on June 26, 1876 and what would prove to be his last battle, the Battle of Wolf Mountain on January 8, 1877. Two Moons’ defeat in the battle at Wolf mountain by General Nelson A. Miles would inevitably lead to the surrender of his Cheyenne band at Fort Keogh in April, 1877.
After the surrender of the Cheyenne band he led in 1877, Two Moons chose to enlist as an Indian Scout for the same General, Nelson A. Miles to whom he had not long since surrendered. As a result of Two Moons’ pleasant personality, the friendliness that he showed towards the whites as well as his ability to get along with the military, General Miles appointed him head Chief of the Cheyenne Northern Reservation. As head Chief, Two Moons would prove to play a crucial role in facilitating the surrender of Chief Little Cow’s Cheyenne band to Fort Keogh.
Two Moons traveled on multiple occasions to Washington, D.C., to discuss and fight for the future of the Northern Cheyenne people and to better the conditions that existed on the reservation. In 1914, Two Moons met with President Woodrow Wilson to discuss these matters. He was one of the models selected for James Fraser’s famous Buffalo Nickel.
Two Moons died in 1917 at his home in Montana at the age of 70. His grave still lies alongside U.S. Route 212, west of Busby, Montana.
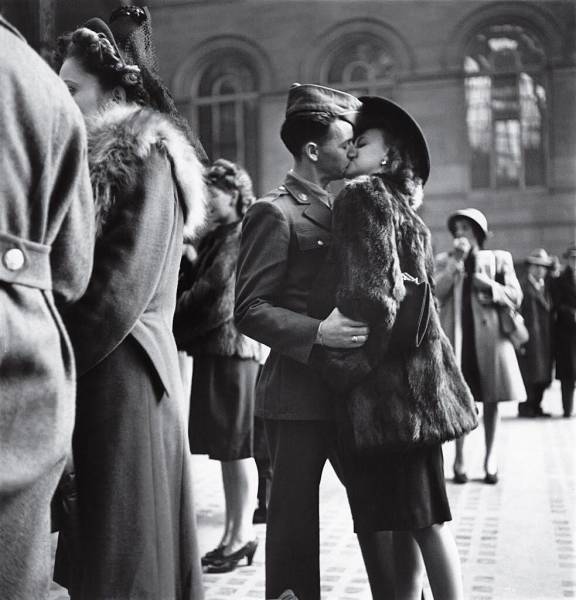
At New York’s Penn Station in 1944, a private moment repeated in public millions of times over the course of the war: a guy, a girl, a goodbye – and no assurance that he’ll make it back
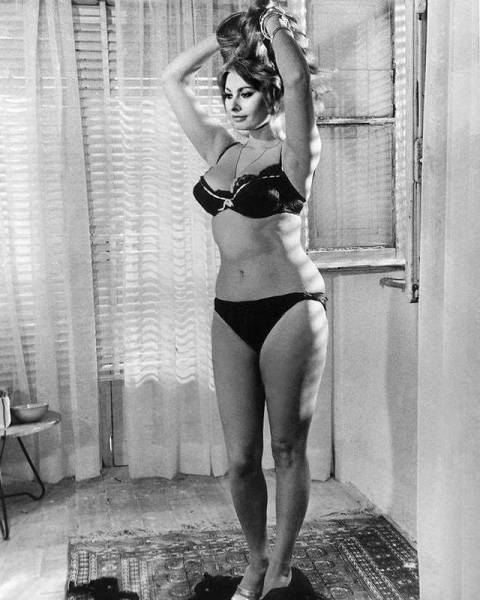
“I’d much rather eat pasta and drink wine than be a size 0.” – Sophia Loren, 1965.